how to read a tympanogram|how to interpret a tympanogram : Manila Learn how to perform and interpret a tympanogram, a test that measures the compliance of the tympanic membrane (TM) with air pressure in the external auditory canal (EAC). See the types and causes . Resultado da O Foco em Loterias desenvolveu uma ferramenta para você conferir sua aposta do Dia de Sorte. Basta você informar a quantidade de dezenas da .
how to read a tympanogram,Tympanograms grade the middle ear function of your patients and appear in a graph format that can take a bit of practice to read! To interpret tympanometry tests, you'll . Tingnan ang higit paLearn how to read and interpret audiogram and tympanogram test results, which measure hearing ability and middle ear functioning. See the classifications and examples of tympanogram types and audiogram .
A tympanogram is the output of performing tympanometry. It is a graphical representation of the compliance of the middle ear as a function of air pressure. Tympanograms are . Tympanometry is a critical tool for diagnosing and evaluating middle ear function. In this article, we will explore what tympanometry is, break down the various .

Learn how to perform and interpret a tympanogram, a test that measures the compliance of the tympanic membrane (TM) with air pressure in the external auditory canal (EAC). See the types and causes . Tympanometry is a test that shows how well your middle ear is working. It does this by measuring how your eardrum moves. Your ear consists of three parts: the .

The correct way to interpret the tympanogram is to read the objective data and report these values as described above. An alternative way is to use Jerger’s . EDWARD ONUSKO, M.D. Am Fam Physician. 2004;70 (9):1713-1720. Tympanometry provides useful quantitative information about the presence of fluid in the middle ear, mobility of the middle ear. Tympanometry is an assessment that measures the middle ear function. It evaluates how the eardrum responds to changes in air pressure within the ear canal. A tympanogram is a graphical .how to read a tympanogram how to interpret a tympanogram 1000 Hz: Tympanogram interpretation. Draw a baseline on the trace at pressure extremes (–400/–600 to +200 daPa) If the trace disappears below the x axis, . Abnormal tympanometry test results may suggest: fluid in the middle ear. perforation of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) scarring of the eardrum, which usually results from frequent ear infections . 1000 Hz: Tympanogram interpretation. Draw a baseline on the trace at pressure extremes (–400/–600 to +200 daPa) If the trace disappears below the x axis, the baseline should be drawn to the x axis, as shown in Figure 1. Identify the main peak, which can occur at any middle-ear pressure. Draw a vertical line from the baseline to the peak .
how to interpret a tympanogram Tympanometry is an assessment that measures the middle ear function. It evaluates how the eardrum responds to changes in air pressure within the ear canal. A tympanogram is a graphical .How To Read A Tympanogram. During the tympanometry test, the probe determines the changes in volume of the ear canal from the probe tip to the eardrum. It then finds the peak pressure of the middle ear system while delivering a 226 Hz probe tone at different levels. A tympanogram displays the ear characteristics listed above in a simple graph.Owing to the shift in the reactance tympanogram, an increase in rate can transform a single-peaked tympanogram into a notched tympanogram. Instrument effect. As the rate of pressure change increases, the rate of immittance change increases, and thus the recording device is more likely to lag the rapidly changing signal that is being measured.Tympanometry tests how well your eardrum moves. The audiologist will put a small probe, which looks like an earphone, into each ear. A small device attached to the probe will push air into your ear. The person testing you will see a graph on the device, called a tympanogram. All you have to do is sit still.how to read a tympanogram The audiogram is a fairly simple graph: The Y-axis (vertical) measures the intensity, or loudness, of the sound. It’s measured in decibels (Db) and ranges from -10 to 110 on the audiogram. Low .Tympanometry is an acoustic evaluation of the condition of the middle ear eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the conduction bones by creating variations of air pressure in the ear canal.. Tympanometry is an objective test of middle-ear function. It is not a hearing test, but rather a measure of energy transmission through the middle ear.It is not a . An audiogram is a hearing test conducted under ideal listening conditions in a soundproof booth. The test includes different pitches and intensities, with the results conveyed in graphical form. If there is hearing loss, an audiogram helps distinguish conductive loss (outer/middle ear) from sensorineural loss (cochlea/cochlear nerve). 1.Tympanometry is a diagnostic procedure that measures the mobility of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the middle ear’s ossicles (tiny bones) in response to changes in air pressure. The test is based on the principle that the compliance of the middle ear system is influenced by variations in pressure. The results of tympanometry are . For information regarding how to use tympanometry as part of a test battery and further reading recommendations, read my blog article on https://wordpress.co.
There are many tests used to detect hearing loss, including tests for the outer, middle, and inner ear. Tests for the outer ear include pure-tone and bone conduction. Middle ear tests include tympanometry, .
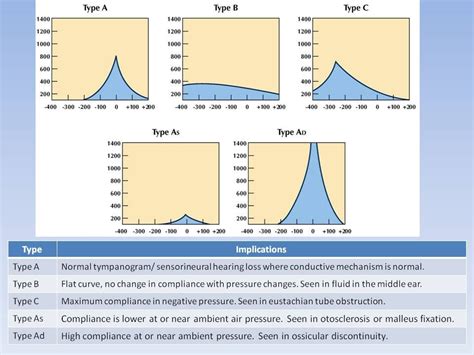
Tympanogram: An objective test that measures the functioning of the middle ear, specifically the mobility of the tympanic membrane and the conduction bones. Acoustic reflex testing: An objective test that measures the contraction of the middle ear muscles in response to loud sounds.Examples of the three most common types of tympanograms are included below: TYPE A: Normal movement of the drum. TYPE B: No movement of the ear drum, most likely due to long standing fluid in the ear or scarring. (Remember B is for bad.) TYPE C: Decreased movement of the ear drum, suggestive of possible fluid in the ear with negative pressure.How to read your hearing test results Please see the graph below, or what we refer to as an ‘audiogram’. You can see lines, one with circles and one with crosses. The line joined together by crosses represents the hearing in the left ear, and the line joined together by circles represents the hearing in the right ear.
Tympanograms ให้คะแนนการทำงานของหูชั้นกลางของผู้ป่วยของคุณและปรากฏในรูปแบบกราฟที่สามารถฝึกอ่านได้! ผลลัพธ์ของ Tympanogram ถูกจัดประเภทเป็น Type A, Type B หรือ Type C .Reading the Audiogram. At first glance, the audiogram may appear to be upside-down. The values on the vertical axis become smaller rather than larger as they move from the bottom to the top of the graph. The numbers on the Y-axis represent sound volume, and are recorded in decibels with the softest sounds at the top and the loudest sounds at .Written by Amplivox. 19/07/2022. Tympanometry is a non-invasive diagnostic test used to assess the health and function of the middle ear. It primarily measures the compliance of the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and the impedance of the middle ear system. The test involves changing air pressure in the ear canal while measuring the eardrum's response.
how to read a tympanogram|how to interpret a tympanogram
PH0 · type ad tympanogram represents
PH1 · tympanometry test cost
PH2 · tympanometry norms asha
PH3 · tympanometry impedance test
PH4 · tympanogram low peak height
PH5 · positive pressure on tympanogram
PH6 · positive middle ear pressure tympanogram
PH7 · how to interpret a tympanogram
PH8 · Iba pa